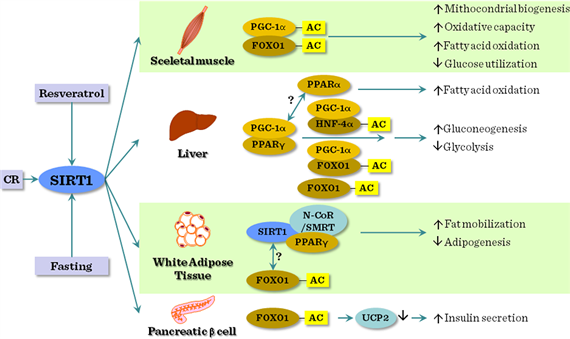
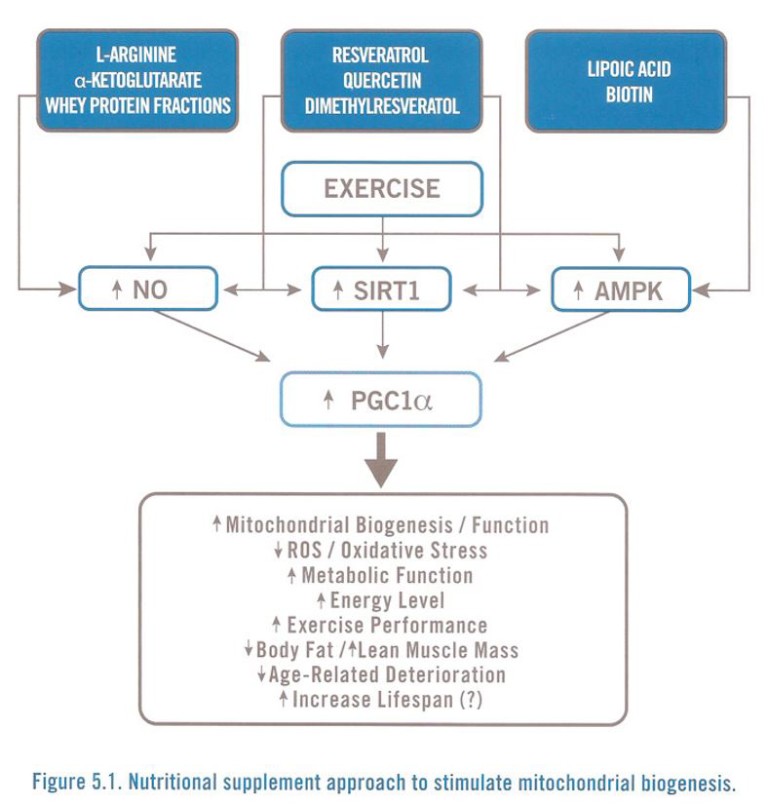
Chronic Fatigue Immune Dysfunction (CFIDS): Increase Energy
Increase the NUMBER of EFFICIENT MITOCHONDRIA (the ENERGY-PRODUCING BATTERIES of the cell) by stimulating “mitochondrial biogenesis-” Your cells need to get rid of large, inefficient mitochondria (from age and/or toxin poisoning) and replace them with smaller, more efficient mitochondria.
Exercise and choose from the above nutrients to stimulate PGC-1a: The”master regulator” of mitochondrial biogenesis.
Contents
RESTORE CELL ENERGY IN THE MITOCHONDRIA
Take 300 mg/day of CoQ10. The scientific literature is now filled with studies documenting the therapeutic power of CoQ10 to limit degenerative disease by boosting mitochondrial health and bioenergetic (energy-producing) capacity.
See also PQQ described below:
Take 10-20 mg/day of PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone) that increases PGC-1a, and which activates genes that govern mitochondrial reproduction, protection, and repair. PQQ also affords potent cardioprotection and optimal defense against neuronal degeneration.
Take 500 mg/day of Quercetin to increase your mitochondrial PGC-1a. Quercetin increases the enzyme NQO1 which reduces the breakdown of PGC-1a.
Increase “Autophagy” in your cells
with Resveratrol, Dietary Restriction (Fasting, or low calorie dietary planning) and/or Metoformin–All have been shown to improve autophagy in the cells. Autophagey is the way your cells “clean house” and “recycle the trash. Autophagy is one of the cells ways of destroying bad mitochondria (via “mitophagy.”)
Increase NAD+ in the cell
with Elysium’s “Basic”: The science demonstrates that these ingredients, Nicotinamide Riboside and Pterostilbene will increase cell NAD+.: More NAD+ in the cell means more energy for the cell to dispose of inefficient mitochondria and build smaller, more efficient mitochondria.
Decrease CD38 to increase cell energy.
Reducing the energy expended on this energy-expensive process allows more energy for these other repair processes.
CD38 is a very inefficient enzyme and consumes as many as 100 NADs for every one cyclic-ADP-ribose that it makes. For this reason, some experts on CD38 feel that the #1 function of CD38 is to regulate cellular NAD levels.
A strong argument for this theory is the recent discovery that CD38 is found inside the cell as well, bound to membranes on the inner portion of the cell nucleus. Here it could deplete nuclear NAD.
Interestingly, the apple skin-derived flavanoid, apigenin, is a powerful inhibitor of CD38. Treatment of cell cultures with apigenin increased NAD levels in the cells, reduced global acetylation of proteins, and reduced the acetylation of p53 and RelA-p65 subunits of NF-kB.
Here is a list of the foods with the most concentrations of apigenin:
| Value | Per | Nutrient | Food |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13506.20 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Spices, parsley, dried |
| 302.00 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Parsley, raw |
| 8.71 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Peppermint, fresh |
| 5.00 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Thyme, fresh |
| 4.61 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Celery, raw |
| 3.85 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Rutabagas, raw |
| 2.41 mg | 100 grams | Apigenin | Celeriac, raw |
Melatonin has multiple beneficial effects on your mitochondria.
Take 3-5 mg of Melatonin at bedtime.
Melatonin permeates cell membranes and scavenges the ROS (“free radicals”) in the cell cytoplasm, mitochondria and nucleus. In the cytoplasm, melatonin maintains GSH homeostasis. Melatonin also regulates the expression of anti-oxidant enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GRd) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), and downregulates pro-oxidant enzymes, such as the NOSs, particularly the iNOS. Melatonin is accumulated in mitochondria at high concentrations, where it scavenges ROS and RNS. Melatonin also protects cardiolipin from oxidation and prevents respiratory chain complexes, as well as mtDNA from free radical attack, thus ultimately protecting the membrane permeability transition (mPT) pore, thus preventing cell apoptosis.
Reduce Mitochondrial Free Radicals (ROS & RNS)
1. Supplement with oral or liposomal Glutathione–The master free radical neutralizer. Also add 500mg twice daily of Acetyl-L-Carnitine and 200 mg/day of R-Alpha Lipoic Acid that together penetrate and protect the mitochondria
2. Stimulate gene production of antioxidants (by increasing enzymes: glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR) superoxide dismutase (SOD),and Catalase) with:
a. Make use of herbals such as “Protandim” or other Nrf2-stimulating foods & products:
- Cruciferous vegetables,
- Resveratrol,
- Wasabi,
- Turmeric and many others
b. Hawthorn–Especially if there is heart involvement
c. Caloric restriction or intermittent fasting
d. Mild to moderate exercise
3. Take EXTRA Vitamin C and Pycnogenol.
4. Learn to separate activities that produce large amounts of free radicals. For instance, separate eating from exercise.
5. Start your meal with healthy nutrients to promote Liver & GI function. See Detox Liver
Supply vitamins and other supplements
in order to compensate for deficiencies with aging. Among them, are
- biotin,
- K2 (with K7),
- vitamin E and tocotrienols,
- thiamine (vitamin B1),
- riboflavin (vitamin B2),
- Vitamin B6,
- triacylglycerol,
- succinate,
- folate,
- dichloroacetate (DCA),
- selenium
- or a multi-antioxidant and multi-mineral combination.
Finally, Include high “ORAC” foods in your diet
–as these are graded by how well they neutralize the free radicals from a meal–Especially with high protein or high fat meals. Or use high ORAC supplements such as Optiberry or Purple defense.
| Rank | Food | Serving Size | Total Antioxidant Capacity per serving size |
| 1 | Small Red Bean | 1/2 cup dried beans |
13727 |
| 2 | Wild blueberry | 1 cup | 13427 |
| 3 | Red kidney bean | 1/2 cup dried beans |
13259 |
| 4 | Pinto bean | 1/2 cup | 11864 |
| 5 | Blueberry | 1 cup cult- ivated berries |
9019 |
| 6 | Cranberry | 1 cup whole berries |
8983 |
| 7 | Artichoke hearts | 1 cup cooked |
7904 |
| 8 | Blackberry | 1 cup | 7701 |
| 9 | Prune | 1/2 cup | 7291 |
| 10 | Raspberry | 1 cup | 6058 |
| 11 | Strawberry | 1 cup | 5938 |
| 12 | Red Delicious apple | 1 | 5900 |
| 13 | Granny Smith | 1 | 5381 |
| 14 | Pecan | 1 ounce | 5095 |
| 15 | Sweet cherry | 1 cup | 4873 |
| 16 | Black plum | 1 | 4844 |
| 17 | Russet potato | 1 cooked | 4649 |
| 18 | Black bean | 1/2 cup dried beans |
4181 |
| 19 | Plum | 1 | 4118 |
| 20 | Gala apple | 1 | 3903 |
To give you an idea of how ORAC-powerful the spices can be, look at this 2006 list from
Content of redox-active compounds (ie, antioxidants) in foods consumed in the United States
The 50 foods with the highest antioxidant content per 100 grams (< 4 ounces)
| Product | Antioxidant content1 |
|---|---|
| mmol/100 g | |
| Cloves, ground | 125.549 |
| Oregano leaf, dried | 40.299 |
| Ginger, ground | 21.571 |
| Cinnamon, ground | 17.647 |
| Turmeric powder | 15.679 |
| Walnuts | 13.126 |
| Basil leaf, dried | 12.307 |
| Mustard seed, yellow, ground | 10.527 |
| Curry powder | 9.980 |
| Pecans | 9.668 |
| Chocolate, baking, unsweetened | 8.876 |
| Paprika | 8.601 |
| Chili powder | 8.372 |
| Parsley, dried | 7.430 |
| Molasses, dark | 4.900 |
| Pepper, black | 4.444 |
| Artichokes, prepared | 4.237 |
| Chocolate, dark | 4.188 |
| Blackberries | 3.990 |
| Whole-grain cereal | 3.412 |
| Cranberries | 3.289 |
| Pudding mix, chocolate, cook-and-serve | 3.026 |
| Bran cereal | 2.925 |
| Power bar, chocolate flavor2 | 2.757 |
| Chocolates, sugar-free | 2.567 |
| Raspberries | 2.334 |
| Strawberries | 2.159 |
| Blueberries | 2.154 |
| Cabbage, red, cooked | 2.153 |
| Wine, red | 2.135 |
| Barley malt syrup, organic | 2.121 |
| Prunes | 2.018 |
| Cherries, sour | 1.814 |
| Peppers, red, cooked | 1.640 |
| Chocolate cookies with vanilla creme filling | 1.604 |
| Cocoa Krispies cereal3 | 1.558 |
| Chocolate chip cookies | 1.524 |
| Mustard, yellow, prepared | 1.501 |
| Milk-chocolate candy | 1.483 |
| Pistachios | 1.426 |
| Plums | 1.330 |
| Kiwi fruit | 1.325 |
| Corn flakes | 1.255 |
| Coffee | 1.249 |
| Spinach, frozen | 1.226 |
| Flaxseed, ground or milled | 1.125 |
| Rice and corn cereals | 1.121 |
| Toasty peanut crackers | 1.101 |
| Cupcakes, chocolate | 1.059 |
| Grape juice | 1.011 |
http://www.newhealthoptions.org/?page_id=2081